In a nutshell:
- While generative AI is powerful, predictive artificial intelligence will provide stronger business impact by anticipating future customer behavior, customer demand, and other trends.
- Predictive AI uses historical and current data with machine learning to forecast future events accurately.
- Predictive modeling is used in various business functions, such as increasing sales and improving customer experiences.
- Different types of AI-driven predictive models include classification and regression models.
- Predictive AI has numerous use cases across various industries and business departments.
- It's important to evaluate use cases for AI against both practical criteria and their potential to improve workers' quality of life.
Artificial intelligence is part of everyday life now. From robot vacuums to voice assistants to ChatGPT, generative and predictive AI are familiar tools today. ChatGPT reached 100 million users faster than any other app (ever!), and "AI" was even named the word of the year. And in business, the use cases for AI continue to expand, though many companies are playing catch-up.
-
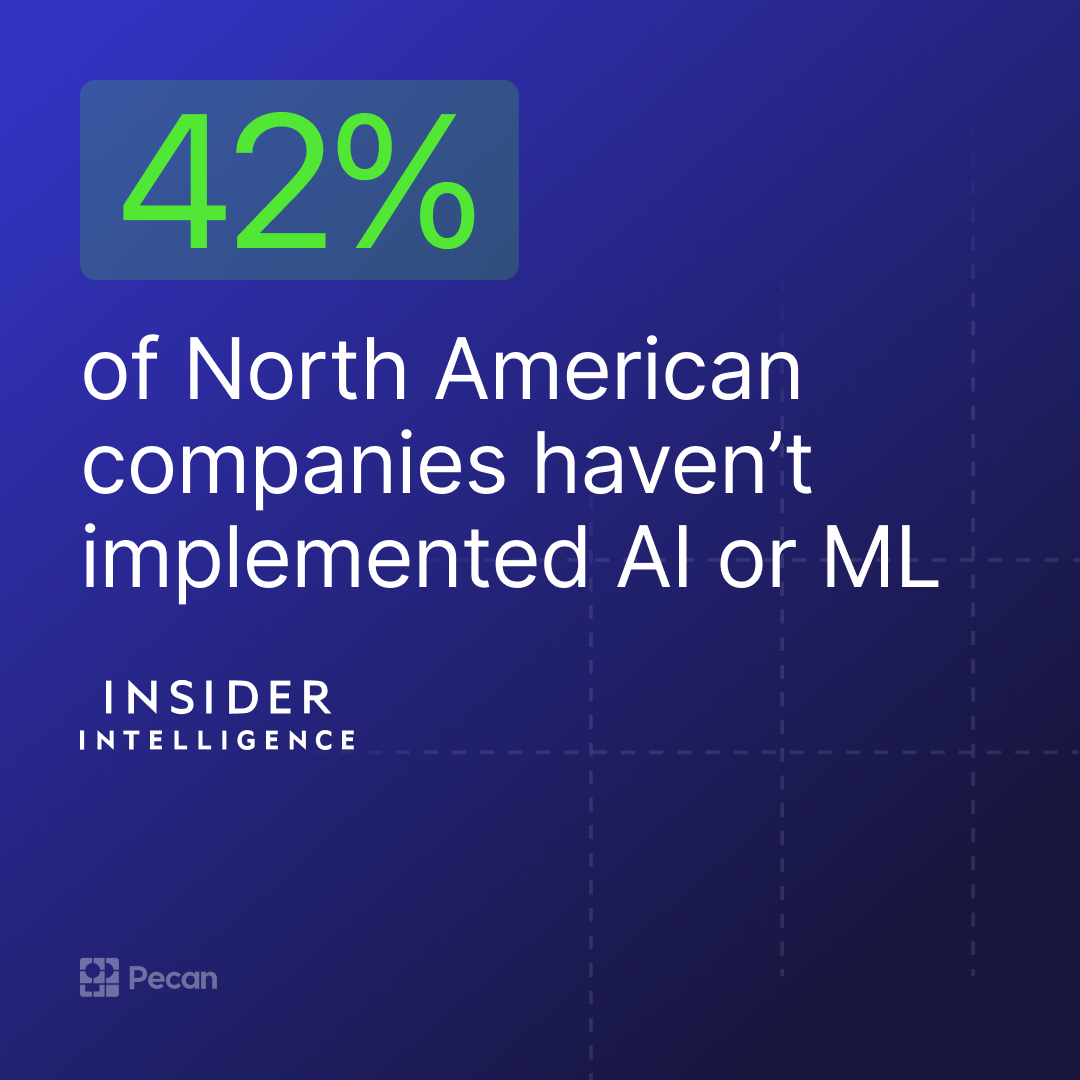
- The implementation of use cases for AI has been slow, but it’s accelerating thanks to new advances.
Some of the leading examples of use cases for AI now include personalized shopping, fraud prevention, personalized customer experiences, smart content creation, automation of administrative tasks, and AI-powered demand forecasting.
But how do all these work? And which tools are most relevant for your business?
While generative AI is extremely cool, for most companies, a more substantial business impact will come from the ability to make predictions with AI about future customer behavior, customer demand, and other trends that will shape their business outcomes.
Let's look at how making predictions with AI could help your team shape more informed decisions and shape a forward-looking, proactive strategy.
Predictive Use Cases for AI
Many businesses have adopted predictive use cases for AI through advanced predictive analytics. Predictive analytics is a computational process that uses historical and current data to identify patterns, apply predictive modeling with machine learning algorithms, and accurately forecast future events.
Focused on the future, predictive modeling differs from other areas of analytics. For example, descriptive analytics draws insights from past events, and diagnostic analytics identifies key trends and relationships among variables in a dataset.
Using a combination of statistics, mathematics, and computation, predictive modeling in business identifies industry-specific patterns and uncovers critical insights that inform various business decisions. Business analytics tools are currently used in multiple functions, including increasing sales, improving customer experiences, and increasing productivity.
Predictive analysis tools are becoming more popular in business because they give decision-makers highly informed projections about future events. As a result, predictive machine learning modeling is becoming the foundation on which companies seize opportunities, grow, and refine existing practices.
There are different types of predictive models, including:
- Classification models. These models describe customers by predicting types or “classes” of outcomes based on historical data. For example, customers could be classified by their potential to churn or respond to special offers. Decision trees are algorithms often used to build classification models that describe customer decisions, allowing them to be divided into groups based on specific variables.
- Regression models. This predictive model projects a specific number, such as a customer's lifetime value (LTV). It generates this prediction by estimating relationships among variables.
So how does this technology work in the real world? There are many use cases.
According to McKinsey, businesses can improve both process efficiency and revenue substantially by implementing the right uses of AI.
Business Use Cases for Predictive Modeling
Predictive modeling is currently applied in a wide range of industries. This technology's uses include refining marketing campaigns, predicting insurance customers' needs, increasing e-commerce sales, and enhancing subscriber retention in direct-to-consumer businesses.
Predictive modeling in marketing departments and companies reveals campaign insights based on demographics, product types, and product brands. The technology is used to analyze both first-party data and third-party data. For example, predictions of consumer preferences and customers’ likelihood to engage with messaging, such as email marketing or a phone call, can provide a competitive advantage. These insights also help companies increase their return on marketing investments while avoiding costly missteps.
Predictive modeling can provide exceptional value for established insurance and insurance tech companies. The technology can predict customer needs and increase the share of wallet by predicting customer behavior. Insurers can use their data to develop proactive strategies that optimize revenue, guide sales personnel, improve customer satisfaction, and facilitate growth.
E-commerce sites and online retail can use predictive modeling to increase their conversion rate through upselling. Using raw data on sales and customer actions, a predictive lead scoring machine learning model can allow sales teams to focus more on leads with the greatest purchasing likelihood. These more focused efforts lead to higher sales volume and value per transaction.
In the mobile app industry, predictive analytics is used to identify potential customers and increase profits. Predictive analytics in mobile apps analyzes user data to inform marketing campaigns and minimize user churn. Mobile app companies can keep customers engaged by providing offers and incentives based on usage patterns. This customer satisfaction results in longer subscriptions and increased in-app purchases.
Direct-to-consumer companies increasingly turn to subscriptions to generate revenue, and predictive analytics can help retain these subscribers, optimizing LTV. Predictive modeling can use historical subscriber data to identify users most likely to churn for many products and direct-to-consumer industries. These models can also optimize upselling efforts, generating more revenue from existing subscribers and improving services.
Use Cases for AI in Other Business Functions
In addition to those use cases, artificial intelligence can streamline and improve business processes across different departments. Here are some examples:
Finance Department:
- Fraud Detection: AI can analyze transaction data to identify patterns indicative of fraudulent activities.
- Risk Assessment: AI machine learning models can evaluate credit risk and provide insights for lending decisions.
- Financial Forecasting: AI can assist in predicting market trends and making investment decisions.
- Regulatory Compliance: AI helps ensure compliance with financial regulations by automating data checks and reporting.
HR Department:
- Resume Screening: AI can automate the initial screening of job applications, saving time for HR teams.
- Employee Onboarding: AI chatbots with natural language processing capabilities can provide accurate information and guidance to new employees.
- Employee Engagement: AI surveys and sentiment analysis can gauge employee satisfaction and provide insights.
- Talent Acquisition: AI can match job candidates with relevant positions and identify top talent.
Operations Department:
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI helps in managing inventory, demand forecasting, and logistics planning.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can predict equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Predictive maintenance catches problems before they occur to enable proactive responses.
- Quality Control: AI can identify defects and anomalies in manufacturing production processes.
- Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle customer inquiries and support.
And those use cases for AI are just the beginning. As the technology continues to improve, there will undoubtedly be new ways to use AI to maximize efficiency, accuracy, and quality across industries and teams.
Which use case should you choose first for AI? Our CEO and co-founder, Zohar Bronfman, offers advice on how to choose the best business process for implementing AI.
What makes a good AI use case?
When you're evaluating different use cases for AI, consider these factors:
- It should address a real-world problem or challenge, such as tasks that are time-consuming, complex, or require large amounts of data analysis.
- You should have access to high-quality, relevant data that's relevant to the use case. AI algorithms rely on data to learn and make accurate predictions or decisions, so they need clean, diverse, and well-labeled data for success. (However, Pecan can assist with data cleaning and preparation, so don't stress too much about that!)
- The AI use case should have a clear and measurable objective, such as benefits or improvements in efficiency, accuracy, or cost savings.
- The use case should be scalable and adaptable to handle increasing data or changing requirements. If you can't continue to scale or update the AI solution, it won't be adopted organization-wide and be sustainable for the long haul.
What Are Use Cases for Generative AI?
We've mostly talked about predictive AI here, but let's touch briefly on generative AI as well. Generative AI is rapidly transforming various aspects of business operations, offering innovative solutions to longstanding challenges. Here are some key use cases for generative AI in business:
- Machine-generated events monitoring: AI systems can continuously track and analyze vast amounts of data, alerting businesses to important events or trends in real time.
- Customer service automation: AI-powered chatbots and virtual customer service agents can handle a wide range of customer inquiries, providing quick and accurate responses 24/7 and potentially reducing human error.
- Document search and synthesis: Generative AI can quickly sift through large document repositories, extracting relevant information, identifying key topics, and summarizing major points for efficient decision-making.
- Product/content catalog discovery: AI algorithms can enhance product recommendations and content discovery, personalizing each user's experience and potentially increasing sales.
- Supply chain advisor: AI can analyze complex supply chain data, predict potential disruptions, and suggest optimizations to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
These applications represent just a fraction of generative AI's potential in business. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative use cases emerge, further revolutionizing how companies operate and compete in the global marketplace.
Watch how Pecan helps you translate your specific use case for AI into a predictive question — then into a machine learning model that can transform your outcomes.
The Value of AI Extends Beyond Use Cases
It's also worth noting that while those measurable improvements are important, there are many other ways that AI can significantly enhance workers' daily lives on the job.
For example, AI can automate routine and repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on more creative and strategic aspects of their roles. It can provide valuable insights and data-driven recommendations, helping employees make informed decisions and improving productivity. AI-driven tools, like virtual assistants and chatbots, offer quick access to information and support, streamlining communication and reducing administrative burdens.
To make jobs less cookie-cutter and encourage stronger performance, AI can enhance personalization. It can tailor work experiences to individual preferences and needs, fostering job satisfaction and a more balanced work-life dynamic.
AI can be a valuable coach by offering personalized skill development and goal-setting guidance. It can provide real-time feedback on work performance and even assist with time and stress management.
Take Your Business to the Next Level with Pecan
Predictive modeling from Pecan can provide impactful, scalable business value to companies in various industries. Using the power of prediction, Pecan’s automated platform can significantly enhance business outcomes faster than any other artificial intelligence solution.
Schedule a demo with us today if you’d like to know more about use cases for AI that will support your business's success.




